CVTE
Diesel Technology
Guy Shepherd, Academy C Administrator – Ext. 113
Course & Program of Studies
Statement of Purpose
The Diesel Technology program at GNBRVTHS is committed to providing students with the skills and knowledge necessary to succeed in the dynamic field of diesel mechanics. Our program focuses on:
- Hands-on Training: Practical experience working on a variety of diesel engines and heavy equipment.
- Industry-Standard Equipment: Access to state-of-the-art diagnostic tools and equipment.
- Safety Training: Emphasizing safety protocols and regulations in the shop environment.
- Technical Skills: Developing a strong foundation in diesel engine theory, diagnosis, and repair.
- Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: Encouraging students to analyze complex problems and develop effective solutions.
- Career Pathways: Guiding students toward successful careers in the diesel industry, including technician, service advisor, and fleet manager roles.
By combining theoretical knowledge with practical skills, our program prepares students for a rewarding career in the diesel industry.
Exploratory Program
The Freshman Diesel Technology Exploratory program provides a solid foundation in diesel technology, introducing students to the fundamentals of the trade. Key areas of focus include:
- Safety: Prioritizing safety in the shop environment, including the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and understanding safety regulations.
- Tool Usage: Learning to use hand tools and power tools safely and effectively.
- Vehicle Systems: Gaining a basic understanding of vehicle systems, including engine, electrical, and hydraulic systems.
- Basic Maintenance: Performing routine maintenance tasks, such as oil changes and tire rotations.
- Hands-On Experience: Engaging in hands-on activities, such as lifting and supporting vehicles, disassembling and reassembling engine components, and performing basic electrical and mechanical tasks.
Through a combination of hands-on work and classroom instruction, students will develop a solid foundation in diesel technology and be prepared to advance to more complex tasks in their sophomore year.
Freshman Program
The Freshman Diesel Technology program provides a solid foundation in the fundamentals of diesel technology. Key areas of focus include:
- Safety: Prioritizing safety in the shop environment, including the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and understanding safety regulations.
- Understanding of industry related tools and equipment while building a basic knowledge of safe use of these tools and equipment.
- Develop a basic understanding at an entry level of fasteners, diesel engines, preventative maintenance inspections including but not limited to basic repairs to the engine, suspension system, brake system, and electrical systems.
- Vehicle Systems: Gaining a basic understanding of vehicle systems, including braking, electrical, and hydraulic systems.
- Basic Maintenance: Performing routine maintenance tasks, such as oil changes and tire rotations.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Understanding how to read and interpret SDS sheets to ensure safe handling of chemicals.
Through a combination of hands-on work and classroom instruction, students will develop a strong foundation in diesel technology and be prepared to advance to more complex tasks in their sophomore year.
Sophomore Program
Diesel Service Technology
The Sophomore Diesel Technology program builds upon the foundational knowledge and skills acquired in the freshman year. Key areas of focus include:
- Safety: Prioritizing safety in the shop environment, including the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and understanding safety regulations.
- Understanding of industry related tools and equipment while building a basic knowledge of safe use of these tools and equipment.
- Vehicle Systems: Gaining a deeper understanding of vehicle systems, including engine, electrical, and hydraulic systems.
- Basic Maintenance: Performing routine maintenance tasks, such as oil changes, filter replacements, and tire rotations.
- Diagnostic Techniques: Using diagnostic tools to identify and troubleshoot vehicle problems.
- Engine Repair: Disassembling and reassembling engine components, such as cylinders, pistons, and connecting rods.
- Hydraulic Systems: Understanding hydraulic systems and performing repairs on hydraulic components.
Through a combination of hands-on training and classroom instruction, students will develop the skills and knowledge needed to work as entry-level diesel technicians. They will be prepared to advance to more complex tasks in their junior and senior years.

Sophomore Related Class 1
Introduction to Diesel Theory
The Sophomore Diesel Technology program builds upon the foundational knowledge and skills acquired in the freshman year. Key areas of focus for engine maintenance include:
- Routine Maintenance: Performing regular maintenance tasks like oil changes, filter replacements, and lubrication.
- Air Intake and Exhaust System Maintenance: Cleaning and inspecting air filters, exhaust systems, and turbochargers.
- Cooling System Maintenance: Inspecting and servicing the cooling system, including radiators, water pumps, and thermostats.
- Electrical System Maintenance: Diagnosing and repairing electrical components, such as alternators, starters, and sensors.
Through a combination of classroom instruction and hands-on experience, students will develop the skills necessary to maintain diesel engines in optimal condition. This knowledge and skills will be essential for a successful career in the diesel industry.

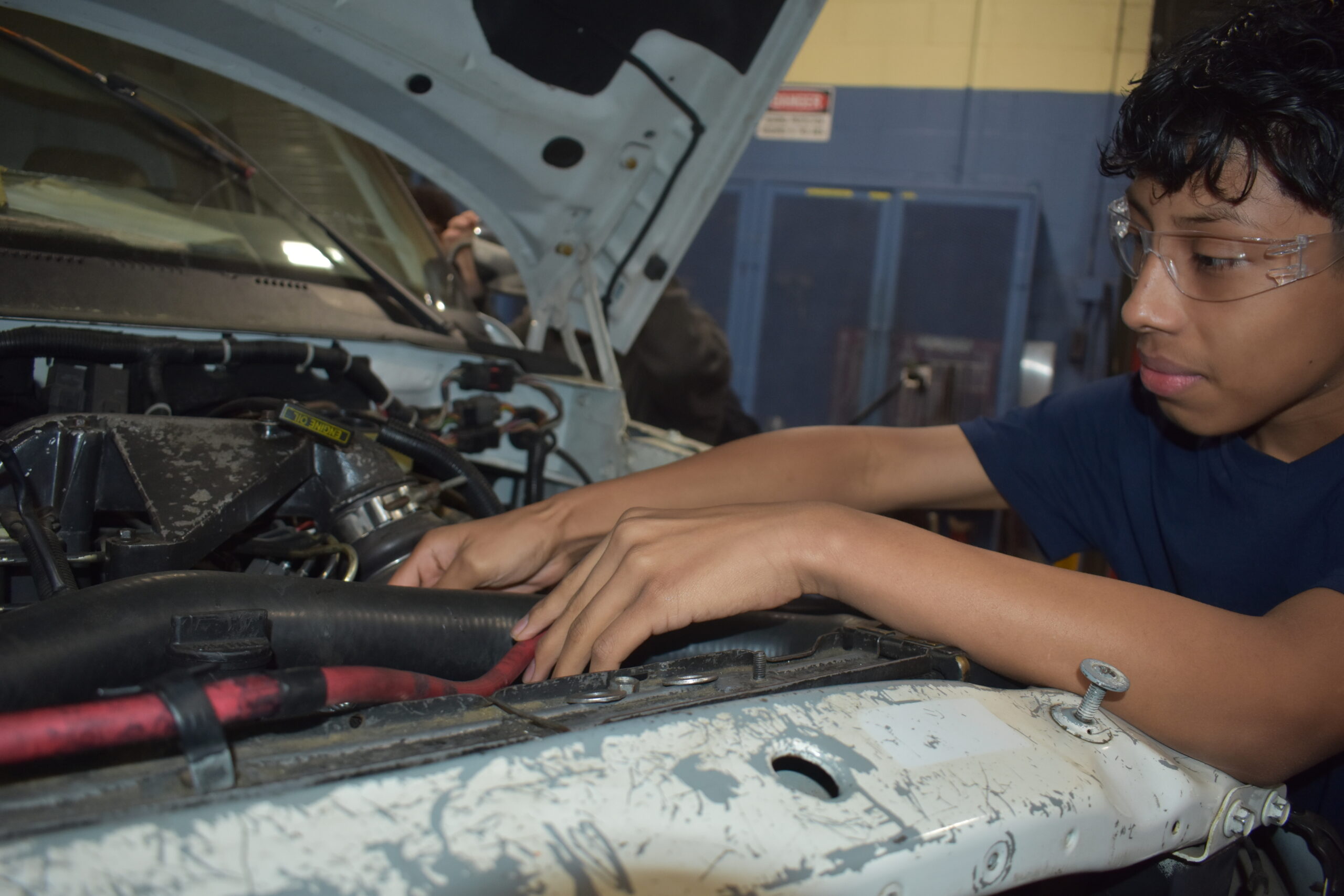
Sophomore Related Class 2
Applied Math
The Sophomore Diesel Technology: Applied Mathematics course provides students with the essential mathematical skills needed to succeed in the diesel technology field. Key areas of focus include:
- Basic Arithmetic: Mastering fundamental operations, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages: Understanding the relationships between these concepts and applying them to practical problems.
- Geometry: Applying geometric principles to measure angles, calculate areas, and solve problems related to shapes and sizes.
- Algebra: Solving equations and inequalities to determine unknown quantities.
- Measurement: Using various measuring tools, such as rulers, tape measures, and calipers, to accurately measure dimensions.
- Technical Math: Applying mathematical concepts to solve problems in diesel technology, including engine calculations, fluid mechanics, and electrical circuits.
By the end of the course, students will be able to:
- Apply mathematical skills to real-world diesel technology problems.
- Use measuring tools accurately.
- Calculate engine performance parameters, such as horsepower and torque.
- Understand and interpret technical drawings and specifications.
- Make informed decisions based on mathematical calculations.
Through a combination of classroom instruction and hands-on application, students will develop the mathematical skills necessary to excel in the diesel industry.
Junior Program
Diesel Service Technology
The Junior Diesel Technology program provides a comprehensive education in diesel technology, preparing students for advanced training and careers in the industry. Key areas of focus include:
- Engine Diagnosis and Repair: Identifying and troubleshooting engine problems, including fuel system issues, electrical faults, and mechanical failures.
- Transmission and Drivetrain Repair: Diagnosing and repairing transmission and drivetrain components, such as clutches, gears, and differentials.
- Electrical Systems: Understanding and repairing electrical systems, including wiring harnesses, sensors, and control modules.
- Hydraulic Systems: Diagnosing and repairing hydraulic systems, such as hydraulic brakes and power steering systems.
- Braking Systems: Inspecting, adjusting, and repairing brake systems, including drum brakes and disc brakes.
- Suspension and Steering Systems: Diagnosing and repairing suspension and steering components, such as shocks, struts, and tie rods.
- Safety Practices: Adhering to safety protocols and regulations in the shop environment.
- Industry Standards: Understanding and applying industry standards and best practices.
Through a combination of classroom instruction and hands-on training, students will develop the skills and knowledge necessary to become skilled diesel technicians. By the end of the junior year, students will be well-prepared to advance to more complex tasks in their senior year.

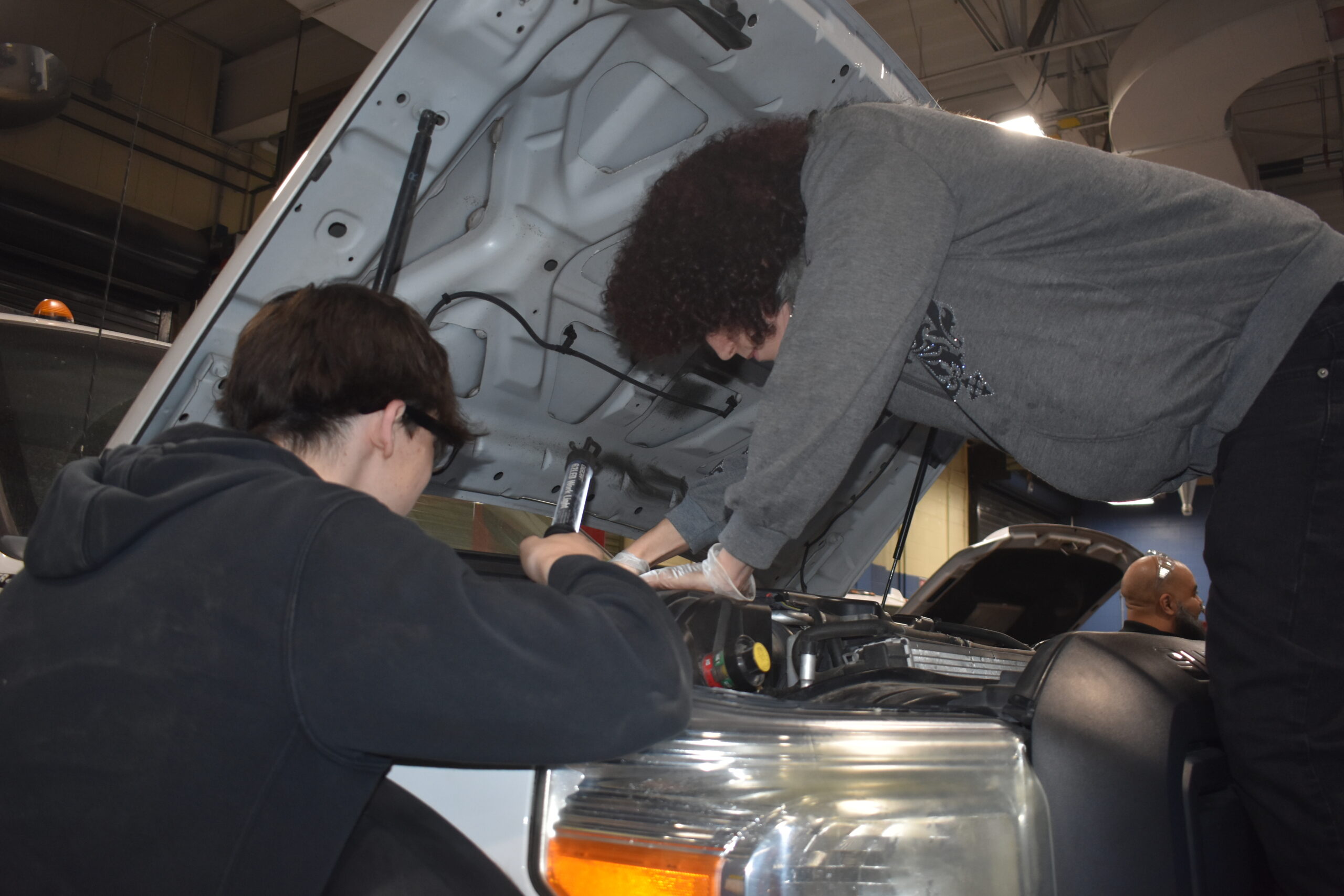
Junior Related 1
Diesel Theory
The Junior Diesel Technology program builds upon the foundational knowledge and skills acquired in the previous years. Key areas of focus include:
- Engine Diagnosis and Repair: Utilizing advanced diagnostic tools to troubleshoot complex engine problems and perform engine rebuilds.
- Heavy-Duty Truck Systems: Understanding the unique characteristics of heavy-duty trucks, including diesel engines, transmissions, and braking systems.
- Hydraulic Systems: Diagnosing and repairing hydraulic systems
- Emissions Systems: Understanding and servicing emission control systems, such as exhaust aftertreatment systems and diesel particulate filters.
- Safety and Environmental Regulations: Adhering to safety regulations and environmental standards in the diesel industry.
- Industry Standards and Best Practices: Staying up-to-date with industry standards and best practices.
Through a combination of classroom instruction and hands-on training, students will develop the skills and knowledge necessary to become skilled diesel technicians. By the end of the junior year, students will be well-prepared to advance to more complex tasks in their senior year. and consider further education at technical schools or colleges.
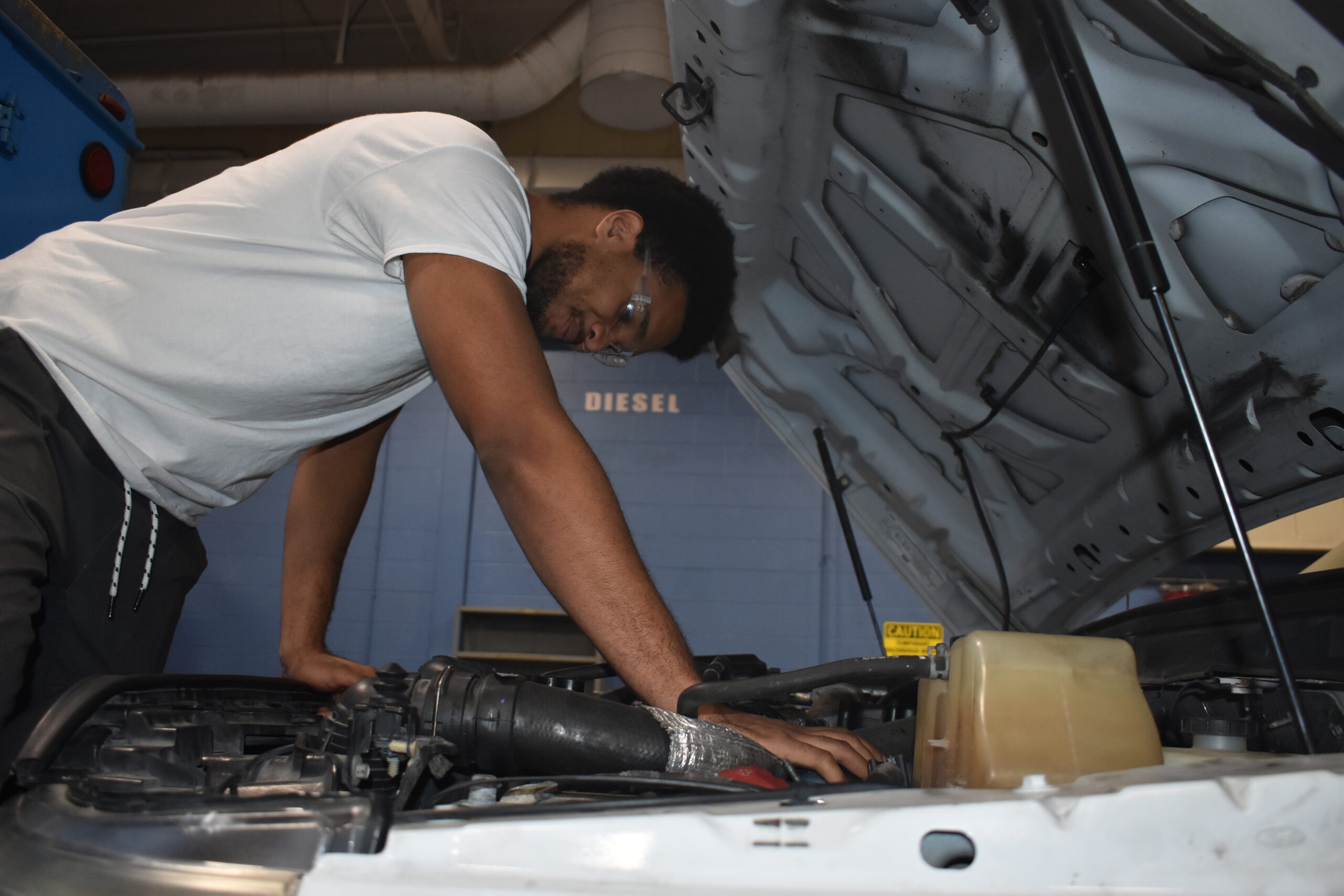
Junior Related 2
Introduction to Diesel Electrical Math
This course focuses on the electrical systems of diesel vehicles, including:
- Basic Electrical Principles: Understanding Ohm’s, and basic circuit analysis.
- Electrical Components: Identifying and diagnosing common electrical components, such as batteries, alternators, starters, sensors, and actuators.
- Wiring Diagrams: Reading and interpreting wiring diagrams to troubleshoot electrical issues.
- Diagnostic Tools: Using diagnostic tools, such as scan tools and multimeters, to identify and diagnose electrical faults.
- Electrical Troubleshooting: Applying systematic troubleshooting techniques to isolate and repair electrical problems.
- Electrical Repairs: Performing electrical repairs, including replacing faulty components, splicing wires, and soldering connections.
By the end of this course, students will be able to diagnose and repair a wide range of electrical problems in diesel vehicles, ensuring their safe and efficient operation.
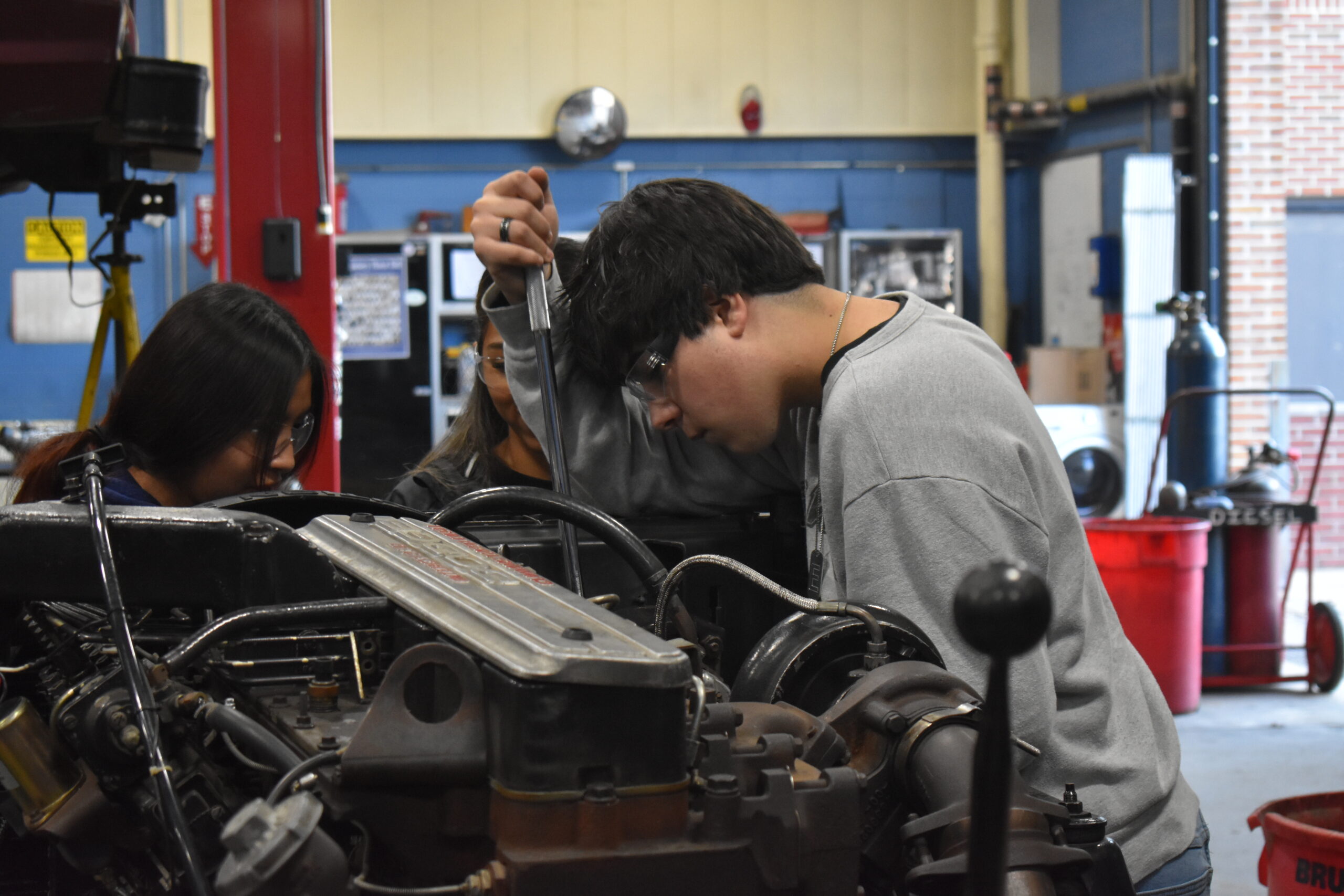

Senior Program
Diesel Service Technology
The Senior Diesel Technology program builds upon the foundational knowledge and skills acquired in previous years. Key areas of focus include:
- Advanced Engine Diagnosis and Repair: Utilizing advanced diagnostic tools to troubleshoot complex engine problems, including engine performance issues, emissions problems, and mechanical failures.
- Heavy-Duty Truck Systems: Understanding the unique characteristics of heavy-duty trucks, including engine configurations, transmission systems, and braking systems.
- Hydraulic Systems: Diagnosing and repairing complex hydraulic systems, such as hydraulic brakes and power steering systems.
- Electrical Systems: Troubleshooting advanced electrical systems, including wiring diagrams, multiplex systems, and electronic control modules.
- Emission Control Systems: Understanding and servicing emission control systems, such as diesel particulate filters (DPFs) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems.
- Safety and Environmental Regulations: Adhering to safety regulations and environmental standards, including hazardous materials handling and disposal.
- Industry Standards and Best Practices: Staying up-to-date with industry standards and best practices.
- Industry Certifications: Preparation for industry certifications, such as ASE certifications, to validate skills and knowledge.
Through a combination of classroom instruction and hands-on training, students will develop the skills and knowledge necessary to become skilled diesel technicians. By the end of the senior year, students will be well-prepared to enter the workforce or pursue further education in diesel technology or related fields. They will be able to diagnose and repair complex diesel vehicle systems and meet the demands of the modern diesel industry.
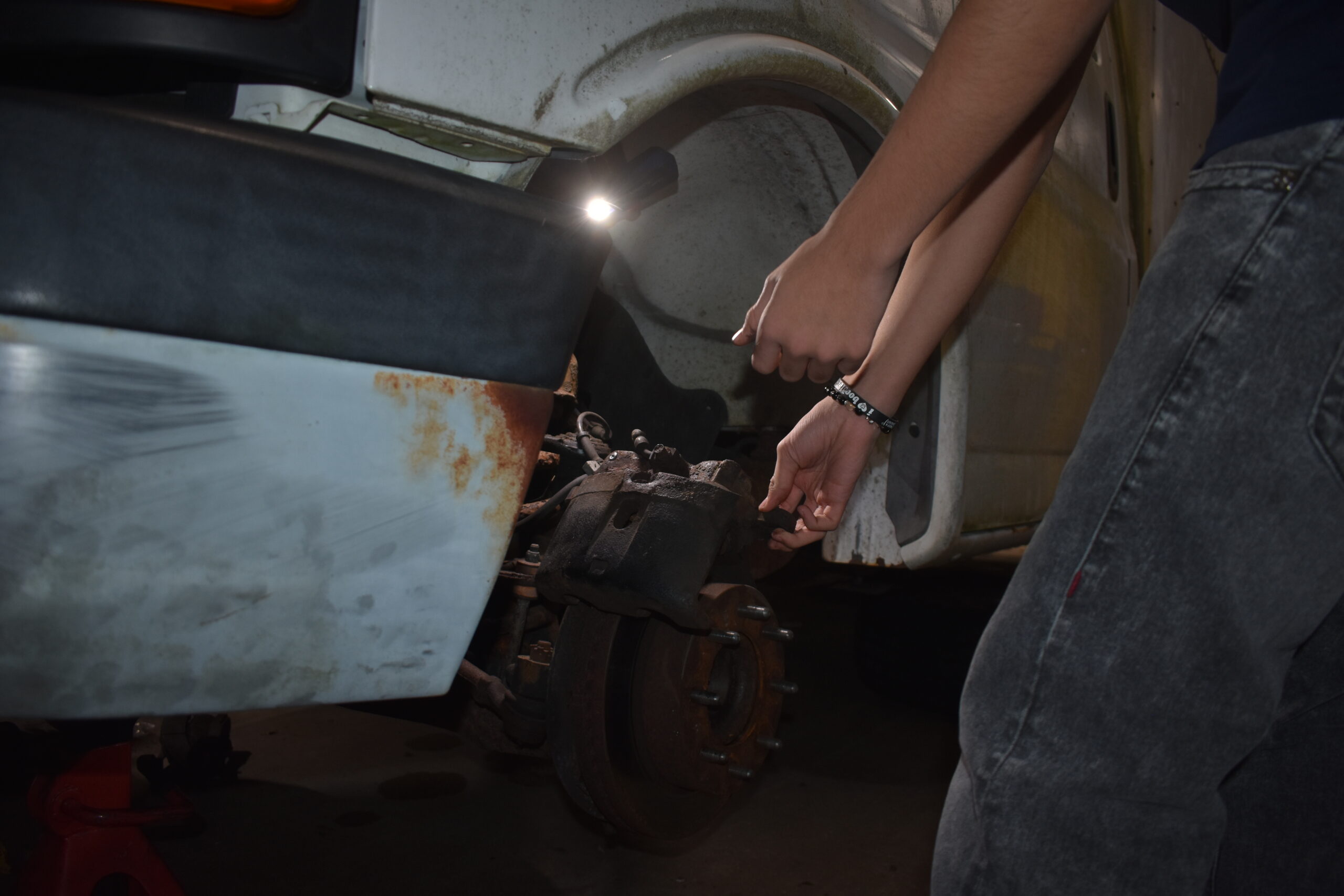

Senior Related 1
Advanced Diesel Theory
The Senior Diesel Technology program provides advanced training in diesel technology, preparing students for careers in the industry. Key areas of focus include:
- Advanced Engine Diagnosis and Repair: Utilizing advanced diagnostic tools to troubleshoot complex engine problems, including engine performance issues, emissions problems, and mechanical failures.
- Heavy-Duty Truck Systems: Understanding the unique characteristics of heavy-duty trucks, including engine configurations, transmission systems, and braking systems.
- Hydraulic Systems: Diagnosing and repairing complex hydraulic systems, including hydraulic brakes and power steering systems.
- Electrical Systems: Troubleshooting advanced electrical systems, including wiring harnesses, sensors, and control modules.
- Emission Control Systems: Understanding and servicing emission control systems, such as diesel particulate filters (DPFs) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems.
- Safety and Environmental Regulations: Adhering to safety regulations and environmental standards, including hazardous materials handling and disposal.
- Industry Standards and Best Practices: Staying up-to-date with industry standards and best practices.
- Industry Certifications: Preparation for industry certifications, such as ASE certifications, to validate skills and knowledge.
Through a combination of classroom instruction and hands-on training, students will develop the skills and knowledge necessary to become skilled diesel technicians. By the end of the senior year, students will be well-prepared to enter the workforce or pursue further education in diesel technology or related fields. They will have the skills and certifications to work on a variety of diesel vehicles, including heavy-duty trucks, buses, and off-road equipment.
Senior Related 2
Preventive Maintenance Procedures
The diesel industry is a critical sector that powers various industries, from transportation to airport ground support equipment maintenance and procedures, and marine diesel basics. Diesel training programs play a crucial role in addressing this skill gap by providing individuals with the necessary education and training to enter this in-demand field.
Benefits of Diesel Training Programs
- Reduced Downtime: Well-trained technicians can quickly diagnose and repair issues, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
- Enhanced Safety: Proper training ensures that technicians can identify and address potential safety hazards, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Environmental Impact: Diesel training programs can promote the adoption of environmentally friendly practices, such as proper maintenance and emissions reduction techniques.
- Career Opportunities: Diesel technicians enjoy stable and well-paying careers with opportunities for advancement.
Key Components of a Successful Diesel Training Program
- Core Curriculum: A strong foundation in diesel engine theory, electrical systems, hydraulic systems, airport ground support equipment, marine diesel basics, and engine repair.
- Hands-on Training: Practical experience working on real diesel engines and equipment.
- Industry Certifications: Preparation for industry certifications, such as ASE certifications, to validate skills and knowledge.
- Safety Training: Emphasis on safety protocols and procedures to ensure a safe working environment.
- Emerging Technologies: Exposure to emerging technologies in the diesel industry, such autonomous vehicles.
By investing in diesel training programs, communities can develop a skilled workforce, support local businesses, and contribute to the overall economic health of the region.
Certifications
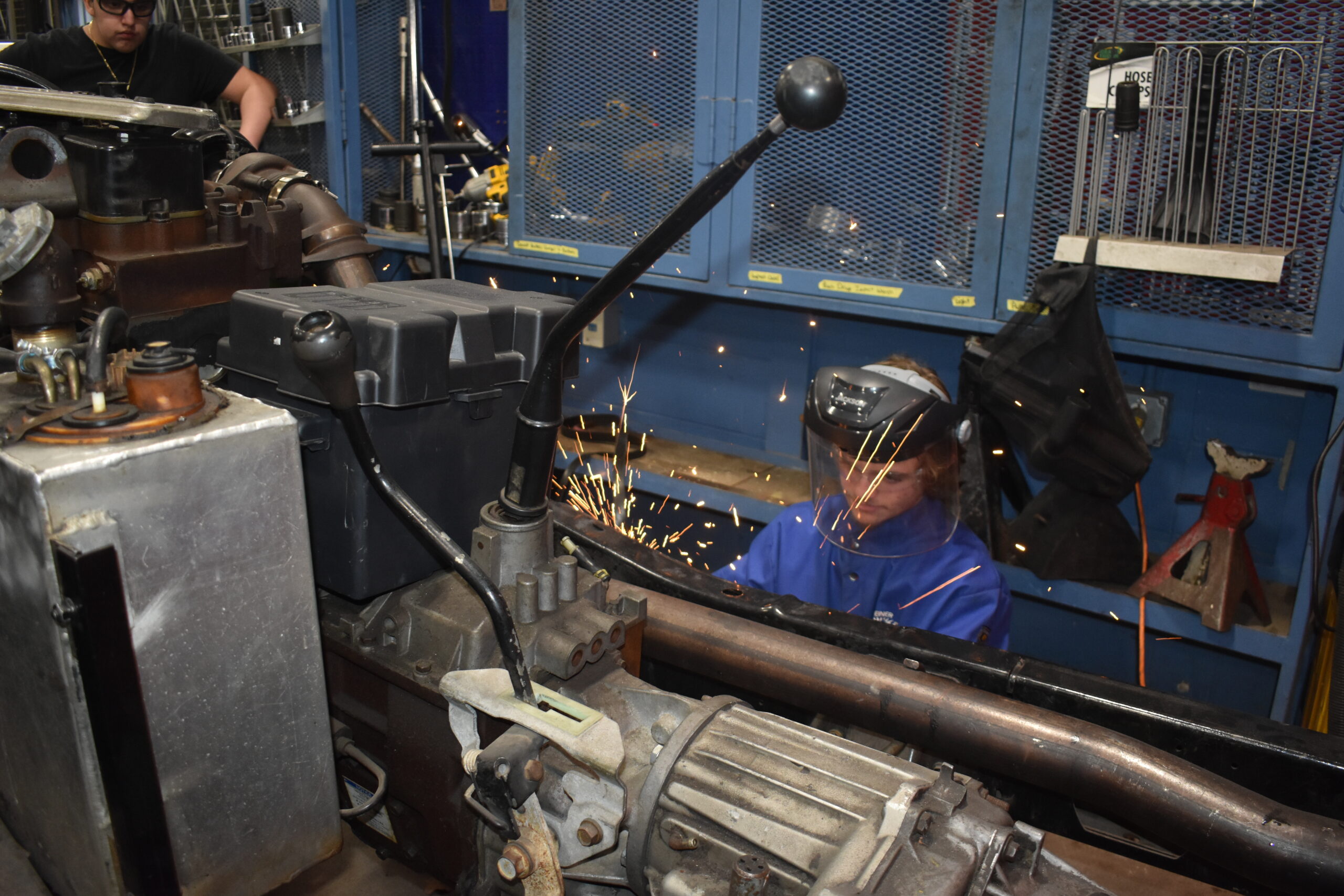

ASE Certifications:
- T2 Diesel Engines
- T4 Brakes
- T6 Electrical/Electronics
Career Opportunities
- Aircraft Body Repairer
- Technical Service Writer
- Parts Department
- New Truck Department
- Used Trucks Department
- Independent Retailer
- Diesel Technician
- Shop Foreman
- Parts Manager
- Finance Manager
- General Manager
- Instructor
- Heavy Equipment Vehicle Designer
- Service Manager
- Repair Shop Owner
- Operations/Safety Supervisor
- Mechanical Engineer
- Manufacturer Engineer
- R & D Engineer
Post-Secondary Education
- New England Institute for Technology
- Massasoit Community College
- Universal Technical Institute
- MassBay Community College
- Wyotech
- MTTI Institute
- IYRS School of Technology and Trades
- MMI
- Cape Cod Community College
- CT Aero Technology School
- Westfield Technical Academy